Google Ads conversion tracking with Google Tag Manager
Updated: Monday, March 31, 2025
What is a Google Ads conversion?
A Google Ads conversion is an important event to be analyzed and optimized in your website visitors’ journey. It can be an event that has a direct or indirect impact on your company’s revenue.
For an e-commerce website, it’s the purchase event that’s the most important to track.
However, for a lead generation website, it’s more likely to be form submissions.
What are Google Ads conversions used for?
In Google Ads, conversions allow you to understand which events are attributed to Google advertising.
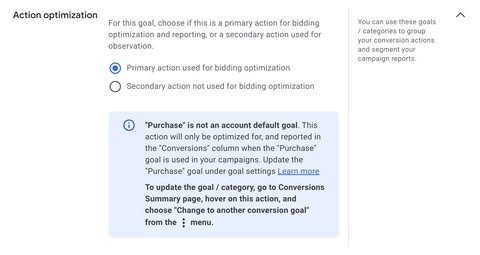
There are two types of conversion actions in Google Ads:
- primary conversions
- secondary conversions
Here’s a table comparing these two types of conversion:
| Primary conversion | Secondary conversion | |
|---|---|---|
| Goal | Main campaign goal | Additional goal or performance indicator |
| Used for auto bidding | Yes (Google uses it to optimize bids) | No (does not directly impact bids) |
| Performance measurement | Used to evaluate campaign success | Used to track actions of interest |
| Typical examples | Purchase, paid registration, appointment booking | eBook download, button click, page visit |
| Strategic impact | Feeds Google Ads optimization decisions | Helps understand the user journey |
Distinguishing between these 2 types of conversions avoids confusing the signals you’re sending to Google Ads.
What is Google Ads enhanced conversion tracking?
Enhanced conversion tracking is the act of sending user data to Google Ads (e.g. email, phone number) to optimize the match rate between your website visitors and people with a Google account.
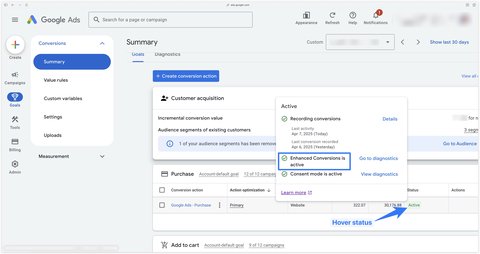
To find out if enhanced conversion is enabled for your conversions, you can hover their status and see if you have the green Enhanced conversions is active tick.
Google Ads native conversions vs. GA4 imports
In my experience, Google Ads native conversions bring up the most conversions (with a similar attribution window).
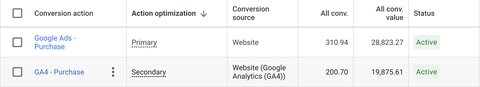
I always recommend using Google Ads native conversions, as I believe that each platform should have its own tracking system and should not be dependent on another platform to work properly.
Requirements for Google Ads tracking
Conversion Linker
The Conversion Linker tag is essential for tracking Google Ads conversions.
Its main role is to detect the presence of the gclid parameter in the page URL, and to set a cookie if this is the case (_gcl_aw). This enables conversions to be attributed to Google Ads.
This tag also deposits another cookie _gcl_au, which is a browser identifier.
To configure the Conversion Linker, go to Google Tag Manager. In the Tags section, click on New.
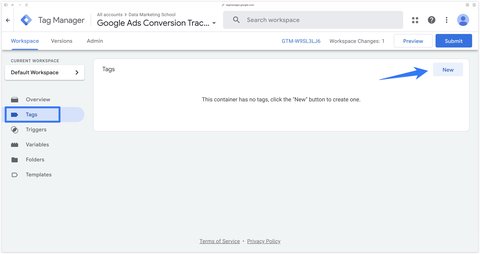
Then select the Conversion Linker from the list of proposed tags.
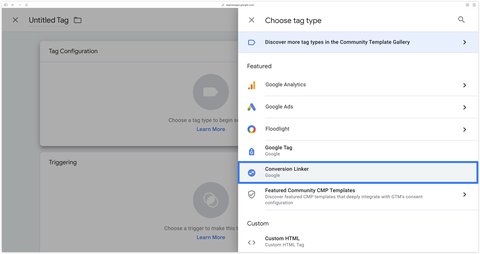
Trigger this tag on Initialization - All Pages.
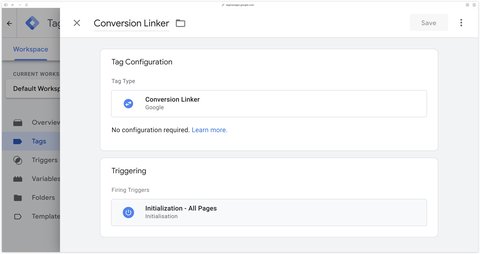
You’ve now finished configuring the Conversion Linker.
Google Consent Mode V2
For Google Ads conversions to work properly it’s also necessary to implement the Google Consent Mode version 2 in order to send the consent signals ad_storage, ad_user_data and ad_personalization.
This is done via the implementation of a CMP such as Axeptio or Didomi.
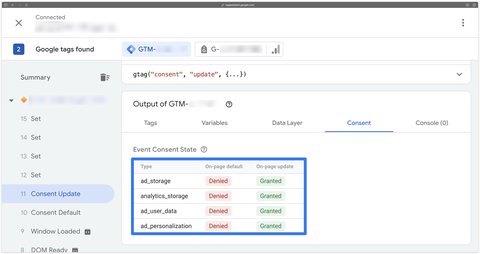
Google AW tag
To send data to Google Ads, you need to set up a Google tag. Go to Google Tag Manager, in the Tags section click on New.

Then select the Google Tag.
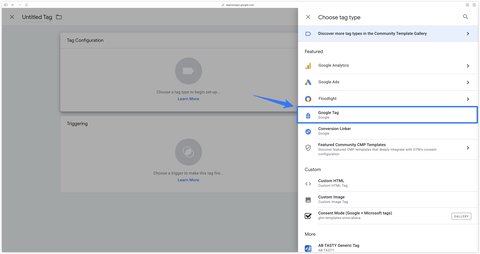
Meanwhile, go to your Google Ads account. In Tools > Data Manager then click Manage next to your Google Tag. Copy your Tag ID starting with AW-.
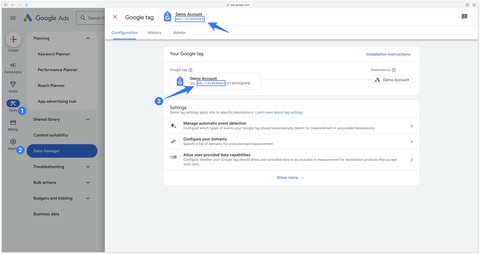
Then paste your Tag ID into the previously selected Google Tag. Trigger this tag on Initialization - All Pages.
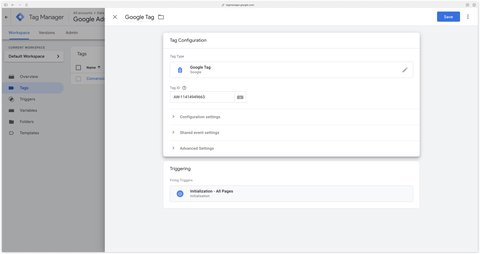
Congratulations, you’ve finished configuring the Google AW tag.
Create a conversion action
In your Google Ads account, go to Goals > Conversions > Summary and click on the Create conversion action button.
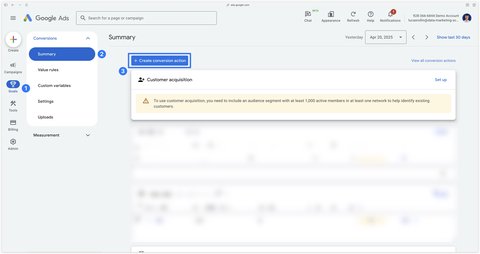
Then select Website.
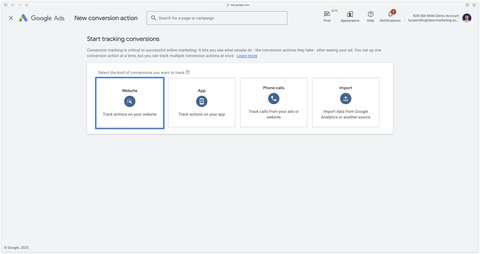
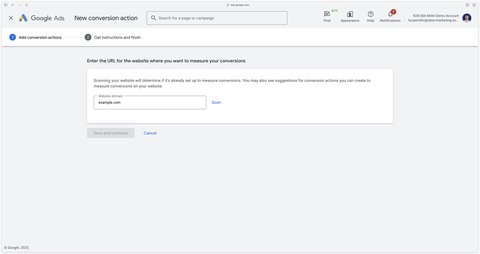
Then you can scan your website or enter example.com to proceed to the next step. Click on Scan.
Scroll to the bottom and click Add a conversion action manually.
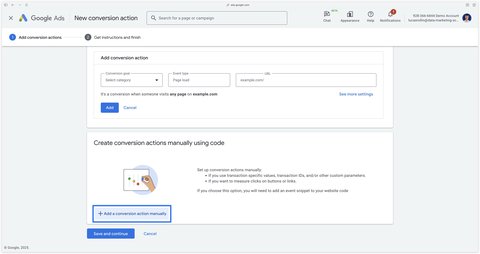
The rest of the tutorial will differ depending on the type of website you have:
Example 1: E-commerce purchase
Conversion action - Purchase
Configure your purchase conversion action in 6 steps:
- Select category Purchase.
- Give your conversion action the name of your choice
- For a purchase, select Use different values for each conversion.
- Enter your average order value as default value (example: 65)
- Count all conversions
- Enable enhanced conversion tracking
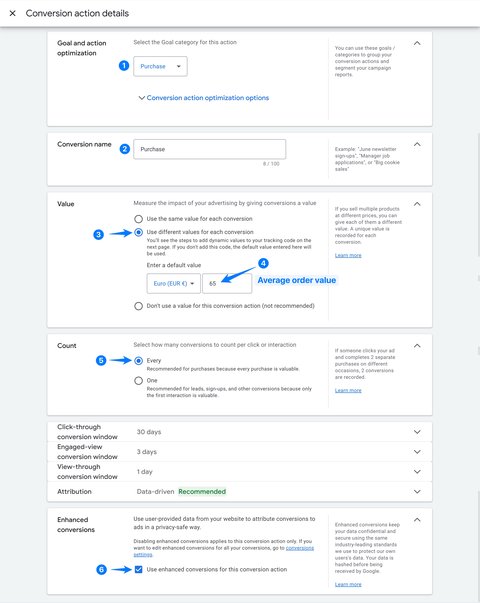
Then click Done and Save and continue.
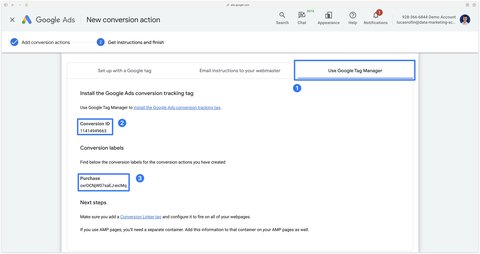
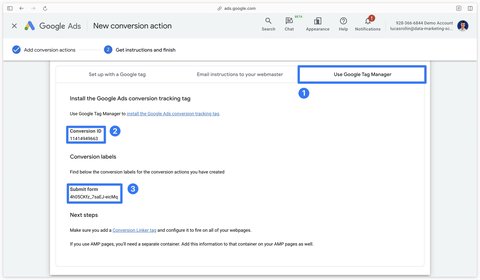
In the Use Google Tag Manager tab, two important pieces of information appear:
- Your conversion ID
- Your conversion label
Put this information aside, as we’ll need it for the rest of this guide.
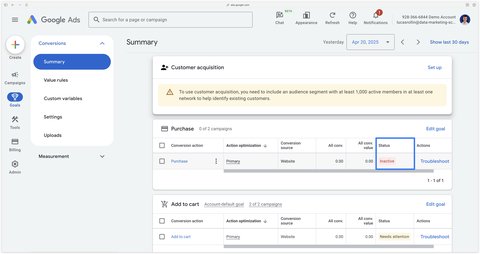
Once created, your conversion action displays the status Inactive.
Congratulations, you’ve completed the creation of a purchase conversion action in Google Ads.
Conversion tracking tag - Purchase
Now that your purchase conversion action has been created, let’s send it some data.
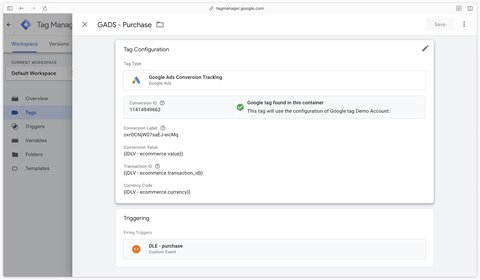
In Google Tag Manager, create a Google Ads Conversion Tracking tag. Then add your conversion identifier and your conversion label (information available in your Google Ads conversion action).
The other tag fields can be filled in from your dataLayer if you’ve set it up.
Example 2: Form submission
Conversion action - Submit form
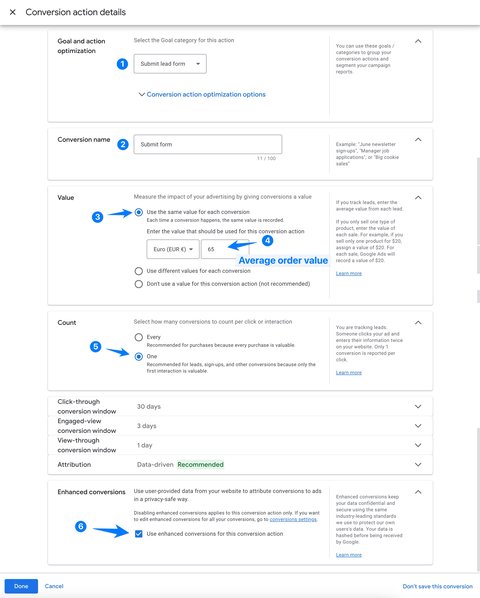
Set up your form submission conversion action in 6 steps:
- Select category Submit lead form.
- Give your conversion action the name of your choice
- For form submission, select Use the same value for each conversion.
- Enter your average lead value as default value (example: 65)
- Count a conversion
- Enable enhanced conversion tracking
Then click Done and Save and continue.
In the Use Google Tag Manager tab, two important pieces of information appear:
- Your conversion ID
- Your conversion label
Put this information aside, as we’ll need it for the rest of this guide.
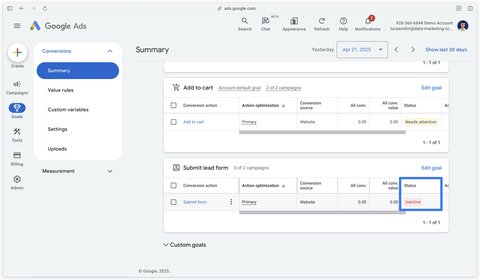
Once created, your conversion action displays the status Inactive.
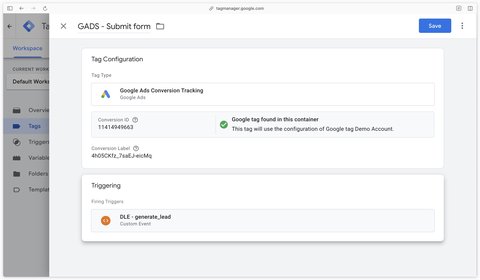
Conversion tracking tag - Submit form
Now that your form submission conversion action has been created, let’s send it some data.
In Google Tag Manager, create a Google Ads Conversion Tracking tag. Then add your conversion identifier and your conversion label (information available in your Google Ads conversion action).
If the value of a lead changes depending on the form used or other parameters, you can fill in a dynamic value in the Conversion Value field.
The trigger here is on a dataLayer generate_lead event, as I’m using a listener that sends this event to the dataLayer on each valid form submission. To find out more, here’s a blog post dedicated to form tracking.
Enhanced conversion tracking
Before configuring enhanced conversion tracking, make sure it’s enabled in Google Ads and managed via Google Tag Manager.
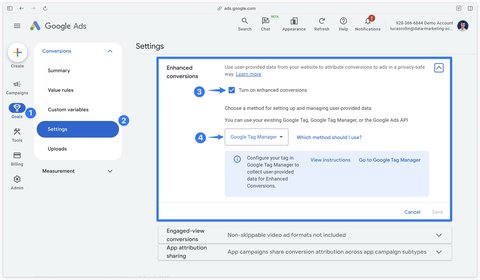
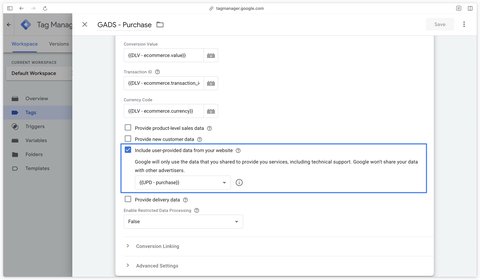
In your Google Ads conversion tag, check the Include user-provided data from your website checkbox.
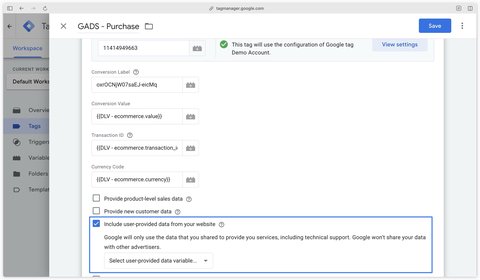
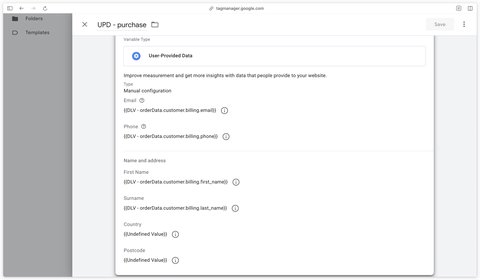
Then create a new User-Provided Data variable, select Manual Configuration as the type.
Fill this variable with all the dataLayer variables you have available.
If you don’t have certain variables available (in this example, I don’t have Country and Postcode), you can create an Undefined Value variable instead, so that you can save your User-Provided Data variable.
Finally, in your Google Ads tag, select the User-Provided Data variable you’ve just created.