Track Single Page Applications with GTM and GA4
Updated: Monday, March 24, 2025
What is a Single Page Application (SPA)?
A Single Page Application is a kind of website that loads all the code required for navigation from the very first page. As the name suggests, it’s an application that consists of a single page.
SPAs are created from the Javascript frameworks such as Angular, React, Vue.js or Next.JS (non-exhaustive list).
Google Analytics 4 offers a default feature to track SPAs, but this may not work for your SPA. That’s why I’m going to show you 3 different methods in this blog post.
What is the History API in Javascript?
Without going into the technical details, the idea here is to understand how SPAs work.
The history object is a global Javascript variable used by most SPAs to manipulate browsing history.
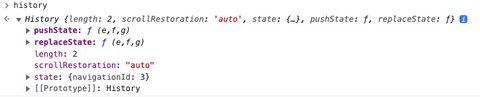
If you’re working on an old SPA, it may not use the Javascript History API, in which case you’ll need to install Google Analytics 4 via method 3.
3 ways to track Single Page Applications with GTM and GA4
Method 1: Leave GA4 with default settings
Let’s see what happens if I install a new GA4 property on all pages.
I now receive History events (gtm.historyChange-v2) and History Change events (page_view).
The gtm.historyChange-v2 event is triggered as many times as the gtm.historyChange event, because they listen to the same events (those of the History API).
However, gtm.historyChange-v2 is managed by GA4, whereas gtm.historyChange is managed by GTM.
This is why gtm.historyChange-v2 then triggers a page_view event (named History Change in GTM).
This page_view event then tracks all pages viewed using the history API.
This feature is enabled by default in GA4’s enhanced measurement, and can be disabled if you feel it’s necessary. If you wish to pass more information in the page_view event such as a dynamic page title, you will need to use method 3.
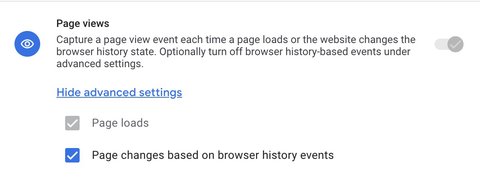
Method 2: Track page views with the History Change trigger in GTM
Disable GA4 automatic detection
To use this method, I disable page tracking when changing the browsing history in GA4’s enhanced metrics settings.

I now only have the gtm.historyChange event, the gtm.historyChange-v2 event is no longer available in the dataLayer.
Disable page_view event in the Google tag

The page_view event
On first page load
This is the most important event to configure correctly, as it will have a direct impact on your traffic sources in GA4.
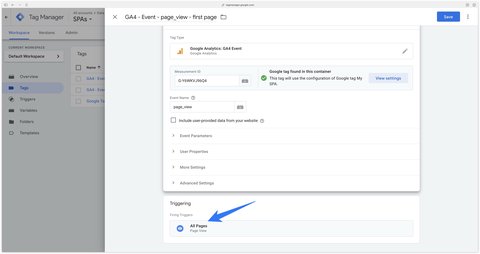
When history changes

Other events
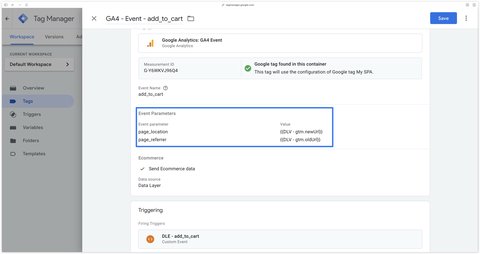
Method 3: Track page views via the dataLayer
This method is recommended because it allows more flexibility. In fact, you’re no longer dependent on your Single Page Application’s history change events. You can trigger a page_view event whenever you like and with the parameters of your choice.
Method 3 involves asking a developer to send a page_view event in the dataLayer on the first page load AND when the user changes view in the SPA.
dataLayer.push(
{
event: "page_view",
virtual_page_title: document.title,
virtual_page_location: document.location.protocol + '//' +
document.location.hostname +
document.location.pathname +
document.location.search,
virtual_page_referrer: document.referrer
}
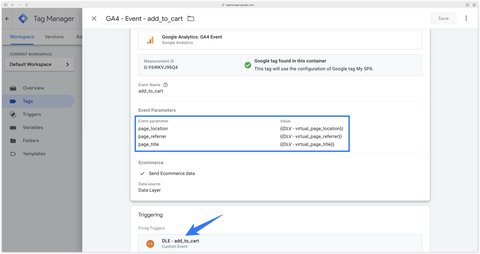
);Once the dataLayer has been set up by the developer, you need to update all my GA4 events to override the page_title, page_location and page_referrer parameters using the variables sent in the dataLayer.
Note here that we’re adding the page_title parameter since we have more flexibility using method 3. This will allow us to have different page titles in GA4.
Disable GA4 automatic detection
To use this method, I disable page tracking when changing the browsing history in the GA4 enhanced metrics settings.

Disable page_view event in the Google tag

The page_view event

Other events