Set up Matomo Analytics with Google Tag Manager
Updated: Wednesday, April 30, 2025
Why choose Matomo Analytics?
Arguments FOR using Matomo Analytics
| ✅ Arguments FOR Matomo | Details |
|---|---|
| Privacy | GDPR compliant, consent-exempted data collection possible (under a specific configuration) |
| Data ownership | You retain full control of the data collected |
| Open-source and customizable | Modifiable code, plugins can be added |
| No data sampling | Complete data analysis without extrapolatio |
| Flexible hosting (cloud or self-hosted) | Choice of hosting mode depending on security needs |
Arguments AGAINST using Matomo Analytics
| ❌ Arguments AGAINST Matomo | Detail |
|---|---|
| Less advanced functionality | Lack of predictive tools and advanced visualization |
| Less intuitive interface | Less ergonomic for non-technical users |
| Installation and maintenance required | Self-hosting requires technical skills |
| Less native integrations | Manual integration with other tools (Google Ads, etc.) |
| Potentially high costs (in the cloud) | Traffic-based pricing, can become expensive |
Matomo configuration with GTM
I’ve created 5 tag templates (available in the GTM gallery) to help you send your data to your Matomo instance from Google Tag Manager :
- Matomo Analytics - Configuration
- Matomo Analytics - Actions
- Matomo Analytics - E-commerce Tracking
- Matomo Analytics - Content Tracking
- Matomo Analytics (Server-Side)
In this tutorial, I will detail the client-side implementation (tags 1 to 4). If you’d like to configure Matomo as server-side (tag 5), you can consult this blog post.
Initial configuration
Go to the Google Tag Manager gallery and add Data Marketing School’s Matomo Analytics - Configuration tag to your workspace.
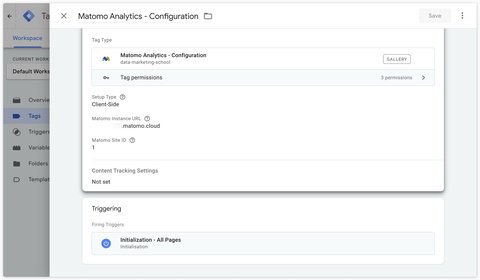
At this stage, you have 3 items to configure:
- Matomo Instance URL: The URL of your Matomo instance.
- Matomo site ID: The site ID of your Matomo instance.
- Trigger: Initialization - All Pages
This tag sends all pages viewed to Matomo.
Actions
Page views
Page views are sent automatically via the configuration tag. If you wish to manage the sending of page views with a separate tag, you can do so with the Matomo Analytics - Actions tag.
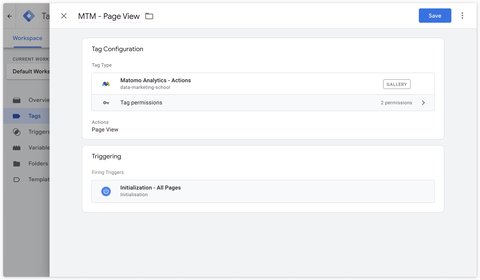
Events
In the Matomo Analytics - Actions tag, select the Event action.
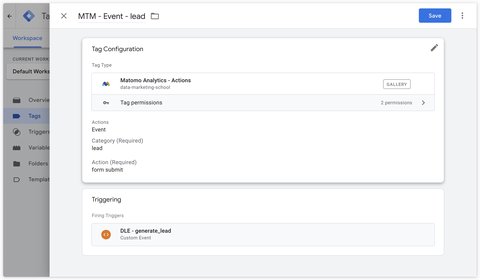
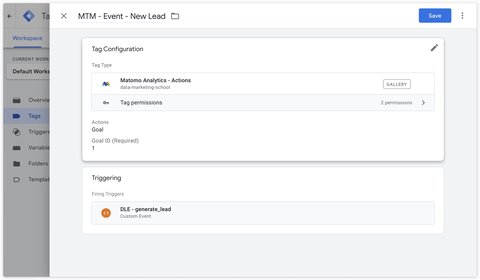
Goals
To send a goal to Matomo, you must first create it in the interface.
Go to Websites > Goals then click on Add a new Goal.
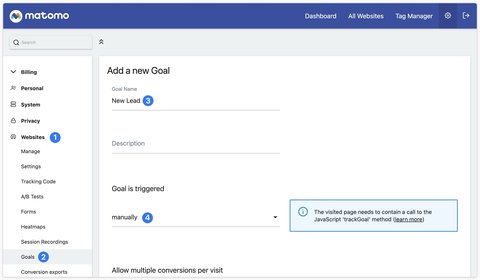
Once your goal has been created, you can retrieve its identifier.

Once you’ve retrieved your goal identifier, all you have to do is specify it in the Matomo Analytics - Actions tag by selecting the Goal action.
Outlinks
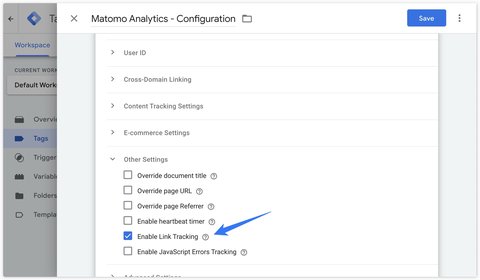
Automatic tracking
To activate automatic outbound link tracking, you can check the Enable Link Tracking box in the Other Settings section of the Matomo Analytics - Configuration tag.
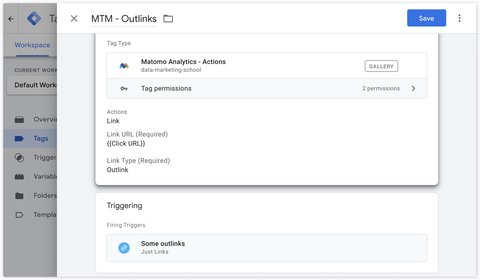
Manual tracking
To track outbound links manually (for example, to track only one of several outbound links, but not all of them) you can use the Matomo Analytics - Actions tag and select the Link then Outlink action as Link Type.
Downloads
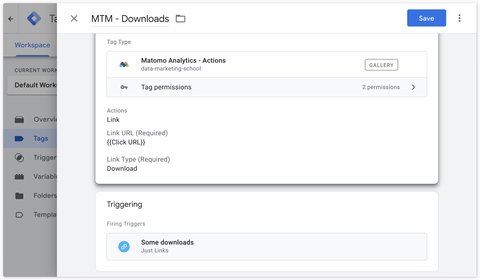
Automatic tracking
To enable automatic tracking of downloads, you can check the Enable Link Tracking box in the Other Settings section of the Matomo Analytics - Configuration tag.

Manual tracking
To track outgoing links manually (for example, to track only one of several outgoing links, but not all of them) you can use the Matomo Analytics - Actions tag and select the Link then Download action as Link Type.
Site search
Automatic tracking
By default, Matomo tracks searches if they generate a page reload and if the results page contains one of the following query parameters:
qqueryssearchsearchwordkkeywordkeywords
Manual tracking
To track searches on your site, you must first activate this feature in Matomo. To do this, go to Websites then Manage.
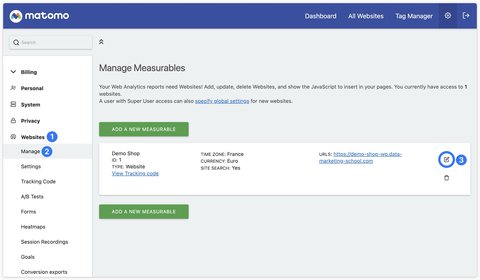
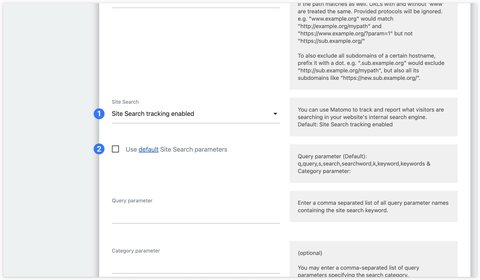
Then click on the icon to edit your website. Scroll down to the Site Search section. Activate Site Search and uncheck the Use default Site Search parameters box.
E-commerce tracking
With e-commerce tracking, Matomo can collect and display detailed statistics on :
- Orders: number, revenue, conversion rate, etc.
- Products: products viewed, added to cart, purchased, their individual performance.
- Cart: abandonments, additions, modifications.
- Revenues by channel: where visitors buy from.
Category views
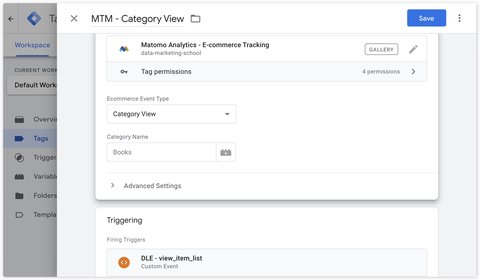
To track category views, you can use the Matomo Analytics - Ecommerce Tracking tag and select Category View as the Ecommerce Event Type.
If you leave the Category Name field empty, the tag will default to the value ecommerce.items.0.item_category if present.
Product views
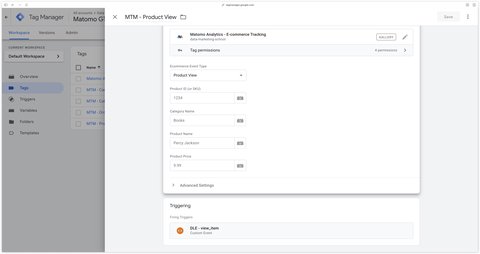
To track product views, you can use the Matomo Analytics - Ecommerce Tracking tag and select Product View as the Ecommerce Event Type.
The other fields are optional and will fetch the following default values:
- Product ID:
ecommerce.items.0.item_id - Category Name:
ecommerce.items.0.item_category - Product Name:
ecommerce.items.0.item_name. - Product Price:
ecommerce.items.0.price
Cart updates
To track cart updates, you can use the Matomo Analytics - Ecommerce Tracking tag and select Cart Update as the Ecommerce Event Type.
By default, this tag will fetch the ecommerce.items array, but you can modify this behavior in the Override items array section.

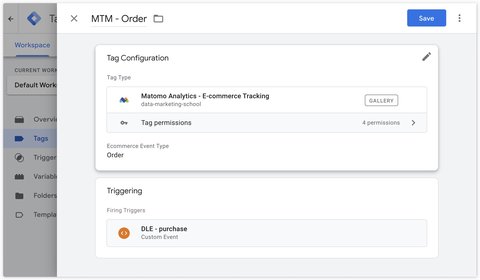
Orders
To track shopping cart updates, you can use the Matomo Analytics - Ecommerce Tracking tag and select Order as the Ecommerce Event Type.
By default, this tag will fetch the following variables from the ecommerce dataLayer:
- Order ID:
ecommerce.transaction_id - Total Revenue :
ecommerce.value - Subtotal: this must be filled in manually, as the standard GA4 dataLayer does not contain this field.
- Tax:
ecommerce.tax - Shipping:
ecommerce.shipping - Discount:
ecommerce.discount
By default, this tag will use the ecommerce.items array, but you can modify this behavior in the Override items array section.
Conclusion
Congratulations, you’ve completed the configuration of Matomo Analytics with Google Tag Manager.
If you encounter any problems in configuring your tags, or if you have any feedback (positive or negative) or suggestions for modifications to share with me, you can do so in the comments below.


